What is an oxygen probe or sensor?
- Utku Inan
- Dec 13, 2024
- 3 min read
It is a sensor used to measure the oxygen concentration of an environment, usually used in industrial applications such as heat treatment furnaces, power plants, cement factories. This device provides information to control systems by monitoring the oxygen level in environments such as furnace atmospheres or combustion processes.

Working Principle of Oxygen Probe
Oxygen probes typically use electrochemical sensor technology and work as follows:
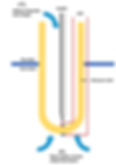
Inside the probe is a semiconductor material such as zirconium dioxide (ZrO₂) , which becomes ionic conductive at high temperatures.
The inside of the probe is filled with pure oxygen or a constant oxygen level (usually air in heat treatment furnaces) as a reference. The outside is exposed to the gas atmosphere (furnace) to be measured.
The transfer of oxygen from the air side to the furnace side creates a voltage potential.
This voltage is calculated using the Nernst equation to measure the oxygen level.
In heat treatment furnaces, this voltage potential and temperature information is transmitted to a controller. The controller calculates the carbon potential , a value that measures the ability of a furnace atmosphere to change or maintain the carbon content in steel.
Calculating Carbon Potential with Oxygen Probe
The conversion of signals from the oxygen probe into carbon potential is based on two assumptions:
The oxygen partial pressure (P₀₂) on the air side of the probe is always assumed to be 21% .
The CO content in the furnace atmosphere is assumed to be 20% .
Both assumptions are considered reasonable for a properly functioning probe operating in an endothermic atmosphere . However, in nitrogen-methanol systems , it is important to verify the second assumption and correct it if necessary.
Oxygen Probe Features
High Temperature Resistance: Most probes can operate at temperatures above 600°C.
Sensitivity: It can measure the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere at ppm level.
Durability: Resistant to harsh conditions such as high temperature, corrosion and abrasion.
Fast Response Time: Responds quickly to changes in oxygen levels.
The main errors encountered in oxygen probes used in heat treatment furnaces are:
Sensor Failures
Aging or Wear: Over the life of the probes, ceramic sensors such as zirconium dioxide may wear out or lose their properties over time.
Thermal Shock: Rapid temperature changes can cause cracks in the ceramic structure of the probe.
Loss of Calibration: Sensors can become inaccurate over time and need to be calibrated regularly.
Chemical Pollution
Contamination of Gases: Oil, carbon or other chemical vapors in the furnace atmosphere can accumulate on the sensor surface and reduce measurement sensitivity. The most harmful of these is the paints applied to the part surface to perform partial cementation in cementation atmospheres.
Oxidation: Chemical reactions occurring in the atmosphere that the probe comes into contact with may affect measurement accuracy.
Assembly and Placement Errors
Incorrect Positioning: Placing the probe in a non-strategic location within the furnace may result in inaccurate measurement of oxygen distribution.
Insufficient Sealing: Lack of sealing at the connection points of the probe may lead to incorrect measurements due to the influence of external gases.
Electrical Problems
Cable Damage: Damage to the connection cables between the probe and the control system may cause problems in signal transmission.
Interference Effect: Environmental electrical interference can disrupt the measurement signal.
Atmospheric Unconformities
Improper Gas Mixture: If the atmospheric gases used in the oven are not in the correct proportions, this will affect the measurement accuracy of the probe.
Carbon Potential Imbalances: Fluctuations in carbon potential in the furnace can reduce oxygen measurement accuracy.
Maintenance Deficiencies
Neglecting Regular Cleaning: Failure to clean the deposits on the probe surface may reduce the measurement accuracy. Carbon combustion is not performed or is not effective.
Inadequate Calibration: Failure to periodically calibrate the probe will result in inaccurate readings.
Turbulence and Gas Flow Problems in the Furnace
Lack of Uniform Distribution: If the oxygen in the furnace atmosphere is not distributed homogeneously, this may cause the probe to take incorrect measurements at different points.
How can BDI Metal help you?
We can select and supply the most suitable probe for your application and furnace system from Leading oxygen probe manufacturer UPC Marathon range. We can check the accuracy of your oxygen probe measurement line and provide information about the health of your probe.

